Explain Mens Rea and the Different Types of Intent
Mens Rea is a Latin term that means Guilty Mind it is the intention or knowledge of the wrongdoing that constitutes a crime we can also call it mental element or psychological element elements that are intangible. Mens rea or guilty intent deals with what the defendant needs to have been thinking at the time he or she committed the actus reus for criminal liability to attach.
It creates criminal liability for the defendant.

. Intention differs from motive or desire Per Lord Bridge R v. Explain mens rea and the different types of intent. Sometimes whether the crime is one for which the death penalty can be given turns.
It is a necessary element the criminal act must be voluntary or purposeful. The main forms of mens rea are intention recklessness and negligence. Most crimes require what attorneys refer to as mens rea which is Latin for a guilty mind In other words what was the defendants mental state and what did the defendant intend when the crime was committedMens rea allows the criminal justice system to differentiate between someone who did not mean to commit a crime and someone who.
Mens rea can be defined as a persons mindset while they carried out an action. It is a necessary element of many crimes. Mens rea is a legal term that generally refers to the guilty mental state the lack of which negates the crime situation on any given occasion.
2310 The majority of cases will be quite straight forward and involve direct intent. The state of mind is verboten explicit or implied in the meaning of any offence. Different types of mens rea.
Please note that the mens rea is not the same thing as motive. Or knowledge that ones action or lack of action would cause a crime to be committed. Mens rea is the mental intention mental fault or the defendants state of mind at the time of the offense sometimes called the guilty mind.
Mens rea refers to the crimes mental elements of the defendants intent. Mens rea or criminal intent is the essential mental element considered in court proceedings to determine whether criminal guilt is present while actus reus functions as the essential physical element. Purpose same as intent knowledge recklessness and negligence.
Describe the legal of essence of criminal conduct. The standard common law test of criminal liability is expressed in the Latin phrase actus reus non facit reum nisi mens sit rea ie. Explain what is meant by direct intention and oblique intention.
Its one of the most important aspects of criminal liability. For a party in a legal case to be found guilty of a crime intent must be proved beyond reasonable doubt. Mens rea simply means guilty mind and denotes fault or culpability of an offence.
Intent refers to the persons mental state and motivation for carrying out a criminal act. Law Latin for guilty mind is the mental element of a persons intention to commit a crime. There are differentlevels of mens rea the highest being intention and the lowest beingrecklessness.
Rather it will be different for each specific crime. In all conventional criminal trials in the United States these two elements Latin terms for culpable mind and culpable action. Mens rea isthe mental element of an offence meaning a guilty mind.
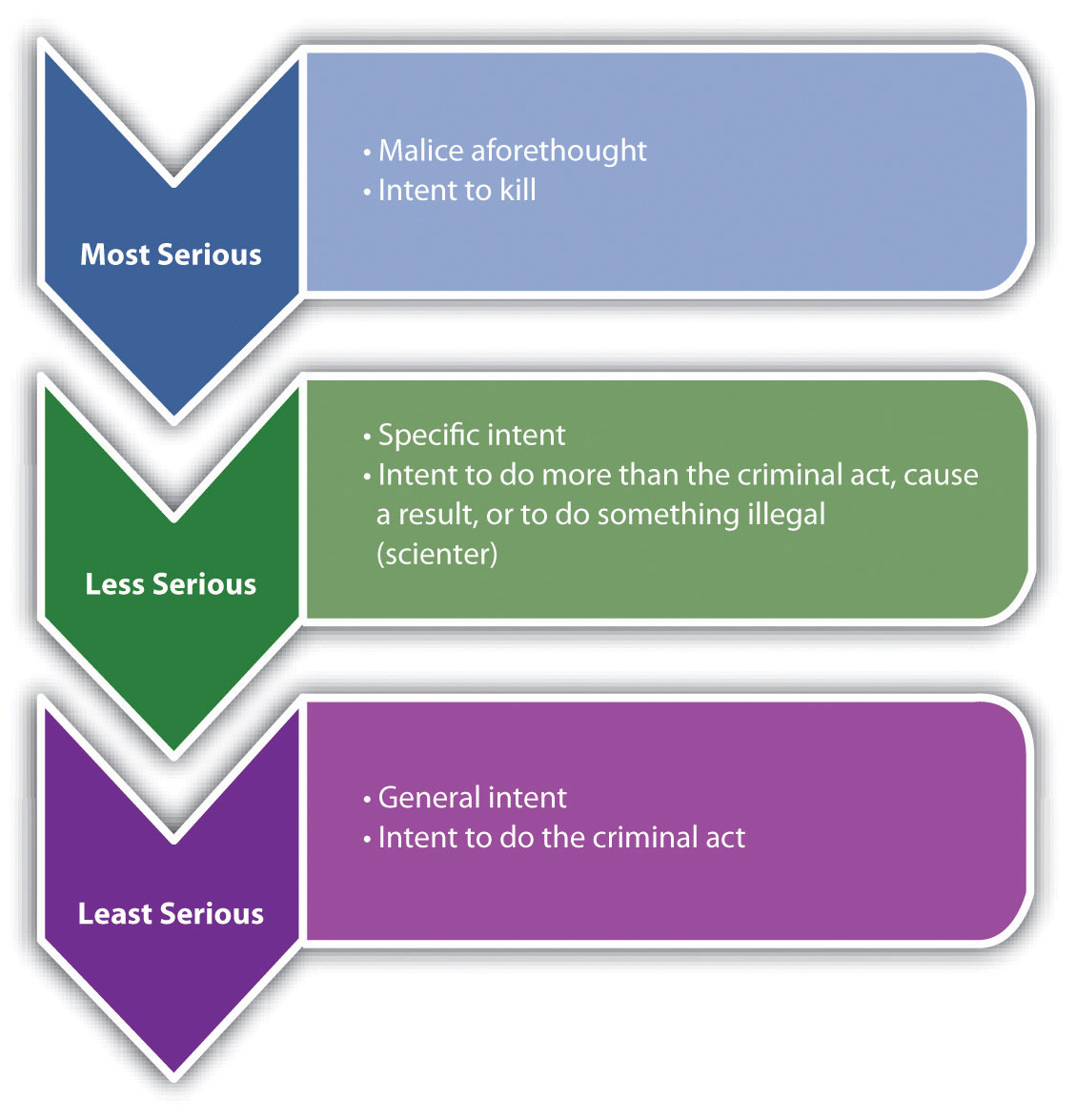
Intention requires the highest degree of fault of all the levels of mens rea. Ulterior Intent Basic Intent and Specific intent It was mentioned above that a consideration of indirect or oblique intent is only really necessary where the offence is one that requires intention as the mens rea elementThese types of offences are known as offences of specific intent - only intention will suffice. Each offence has itsown mens rea in exception of offences of strict liability.
An important comparison of mens rea and actus reus is that while they both involve the offender one involves the mind of the offender while the other involves the physical action or lack of. The mens rea refers to the intent with which the. In the field of criminal justice this term is referred to when someone commits a.
The mens rea is that the defendant must intend to wound or cause grievous bodily harm or intend to resist arrest. In one form of manslaughter the mental element is recklessness only while in a different form of manslaughter the mental element is gross negligence see Chapter 10. To prove intent evidence must show that the act was a deliberate illegal action.
Only when an act is done intentionally that is prohibited by law is it considered a criminal offence. The key feature added by the Model Penal Codes system is that for any criminal statute unless the statute specifically states otherwise the defendant must commit all elements of the crime with a mental state of recklessness or. In all of these cases the question of whether or not a particular defendant had the precise intention necessary for the crime can make a huge difference often a difference of years in prison but sometimes literally a difference of life or death.
The intent which is the driving. Mens rea ˈ m ɛ n z ˈ r eɪ ə. A person who intends to commit a crime can generally be said to be more culpable than one who acts recklessly.
CONDITIONAL INTENT AND MENS REA - Volume 10 Issue 4. Purposely- the person consciously created intent for criminal actions. To be guilty the accused must have the minimum level of mens rearequired by.
Moloney 1985 AC 905 Case summary. The terms subjective and objective mens rea refer to two methods of assessing mens rea. Intermediate 15 The two basic elements of all crimes are the criminal mind mens rea and criminal act actus reus.
Thus a person who kills a loved one dying from a. For this offence the defendant must wound or cause grievous bodily harm. Direct intent can be said to exist where the defendant embarks on a course.
Explain actus reus and what constitutes a criminal act. It is the act of intending meaning to do something. Akid a pharmacist provided confidential information.
The Model Penal Code recognizes four different levels of mens rea. If the defendant did not intend one of these. This can be illustrated by looking at the offence set out in S18 of the Offences Against the Person Act 1861.
In criminal damage and most non-fatal offences against the person such as assault and battery the mens rea is intention or recklessness see Chapters 11 and 16.

4 2 Criminal Intent Criminal Law
Intention Criminal Law Notebook


No comments for "Explain Mens Rea and the Different Types of Intent"
Post a Comment